前言
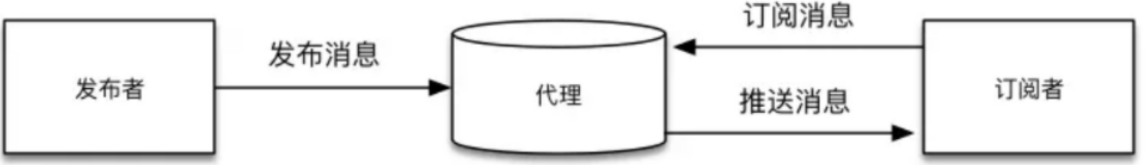
RabbitMQ是一种我们经常使用的消息中间件,RabbitMQ是实现AMQP(高级消息队列协议)的消息中间件的一种,最初起源于金融系统,用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。RabbitMQ主要是为了实现系统之间的双向解耦而实现的。当生产者大量产生数据时,消费者无法快速消费,那么需要一个中间层。保存这个数据。
AMQP,即Advanced Message Queuing Protocol,高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计。消息中间件主要用于组件之间的解耦,消息的发送者无需知道消息使用者的存在,反之亦然。AMQP的主要特征是面向消息、队列、路由(包括点对点和发布/订阅)、可靠性、安全。
RabbitMQ是一个开源的AMQP实现,服务器端用Erlang语言编写,支持多种客户端,如:Python、Ruby、.NET、Java、JMS、C、PHP、ActionScript、XMPP、STOMP等,支持AJAX。用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。
今天这篇,我们来看看Spring Boot是如何集成RabbitMQ,发送消息和消费消息的。同时我们介绍下死信队列。
集成RabbitMQ
集成RabbitMQ只需要如下几步即可
1、添加maven依赖
<!--rabbitmq--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
2、添加配置文件application.yaml
在application.yaml添加配置内容如下
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.1.161 port: 5672 username: guest password: guest cache: channel: size: 10 listener: type: simple simple: acknowledge-mode: auto concurrency: 5 default-requeue-rejected: true max-concurrency: 100 retry: enabled: true # initial-interval: 1000ms max-attempts: 3 # max-interval: 1000ms multiplier: 1 stateless: true # publisher-confirms: true</pre>
注意:
这里最基本的配置只需要配置host,port,username和password四个属性即可
其他属性都有各自的含义,比如retry是用于配置重试策略的,acknowledge-mode是配置消息接收确认机制的。
3、编写配置类
编写RabbitConfig配置类,采用Java Configuration的方式配置RabbitTemplate、Exchange和Queue等信息,具体如下所示
package com.jackie.springbootdemo.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.config.SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration public class RabbitMQConfig implements InitializingBean { @Autowired
SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory simpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
simpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter());
} @Bean("jackson2JsonMessageConverter")
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
} @Bean("rabbitTemplate")
@Scope(ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
@Qualifier("jackson2JsonMessageConverter") Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter) {
RabbitTemplate template = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
template.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter());
return template;
} // --------------------- 声明队列 ------------------------
@Bean
public Queue demoQueue() {
return new Queue("demo_queue");
} // --------------------- 声明exchange ------------------------ @Bean
public DirectExchange demoExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("demo_exchange");
} // --------------------- 队列绑定 ------------------------
@Bean
public Binding bindingAlbumItemCreatedQueue(DirectExchange demoExchange,
Queue demoQueue) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(demoQueue).to(demoExchange).with("100");
} }
注意
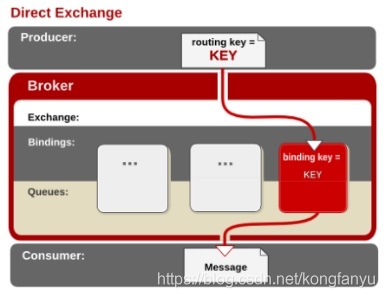
这里声明了Direct模式的Exchange,声明一个Queue,并通过routing-key为100将demo_queue绑定到demo_exchange,这样demo_queue就可以接收到demo_exchange发送的消息了。
4、编写消息发送类
package com.jackie.springbootdemo.message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.support.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class Sender implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback { private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 构造方法注入 */ @Autowired
public Sender(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) {
this.rabbitTemplate = rabbitTemplate;
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this); //rabbitTemplate如果为单例的话,那回调就是最后设置的内容
} public void sendMsg(String content) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("demo_exchange", "100", content);
} /**
* 回调 */ @Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
System.out.println(" 回调id:" + correlationData);
if (ack) {
System.out.println("消息成功消费");
} else {
System.out.println("消息消费失败:" + cause);
}
} }
注意
发送内容content,路由到routing-key为100上,则我们就可以在demo_queue队列中看到发送的消息内容了
confirm函数是回调函数,这里因为没有消费者,且acknoledge-mode是auto(其他两种值分别是none和manual),所以ack是false。
5、编写发送消息测试类
package com.jackie.springbootdemo;
import com.jackie.springbootdemo.message.Sender;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SpringbootDemoApplication.class) @WebAppConfiguration public class RabbitApplicationTests { @Autowired
Sender sender;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws Exception {
sender.sendMsg("test");
} }
运行该测试类,我们可以看到如下结果

6、编写消息消费类
package com.jackie.springbootdemo.message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class Receiver { @RabbitListener(queues = "demo_queue")
public void created(String message) {
System.out.println("orignal message: " + message);
} }
注意
消息消费类也非常简单,添加注解@RabbitListener,指定要监听的队列名称即可
除了注解@RabbitListener,我们经常还能看到@RabbitHandler,这两个注解可以配合起来使用。
@RabbitListener 标注在类上面表示当有收到消息的时候,就交给 @RabbitHandler 的方法处理,具体使用哪个方法处理,根据 MessageConverter 转换后的参数类型,形如
@RabbitListener(queues = "demo_queue") public class Receiver { @RabbitHandler public void processMessage1(String message) {
System.out.println(message);
} @RabbitHandler
public void processMessage2(byte[] message) {
System.out.println(new String(message));
} }
7、运行消息发送测试类

从执行结果可以看到,因为有了消费者,所以这次打印的结果是"消息消费成功"
而且,我们看到Receiver类将消息消费并打印出消息的内容为"test"。
代码已经提交至项目rome:https://github.com/DMinerJackie/rome (本地下载)
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对好代码网的支持。