最近倒腾了一会vue,有点迷惑其中methods与computed这两个属性的区别,所以试着写了TodoList这个demo,(好土掩面逃~);
1. methods
methods类似react中组件的方法,不同的是vue采用的与html绑定事件。
给个例子
/*html*/ <input type="button" value="点击" v-on:click='handlClick' id="app">
/*js*/
var app = new Vue({
el:'#app',
methods:{
handlClick:function(){
alert('succeed!');
},
}
})
通过在input标签中的vue命令 v-on命令绑定handlClick事件,而handlClick事件是写在methods属性里的
2. computed
/*html*/
<div id="app2">{{even}}</div>
/*js*/
var app2 = new Vue({
el:'#app2',
data:{
message:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
},
computed:{
even:function(){ //筛选偶数
return this.message.filter(function(item){
return item%2 === 0;
});
},
},
});
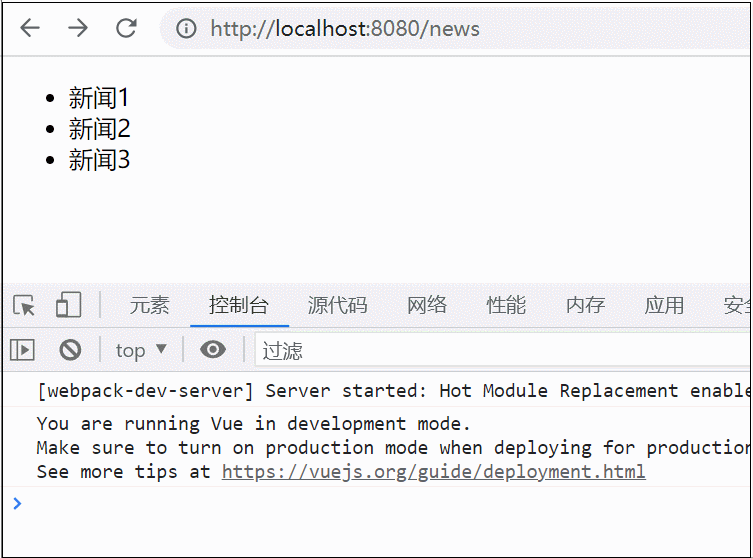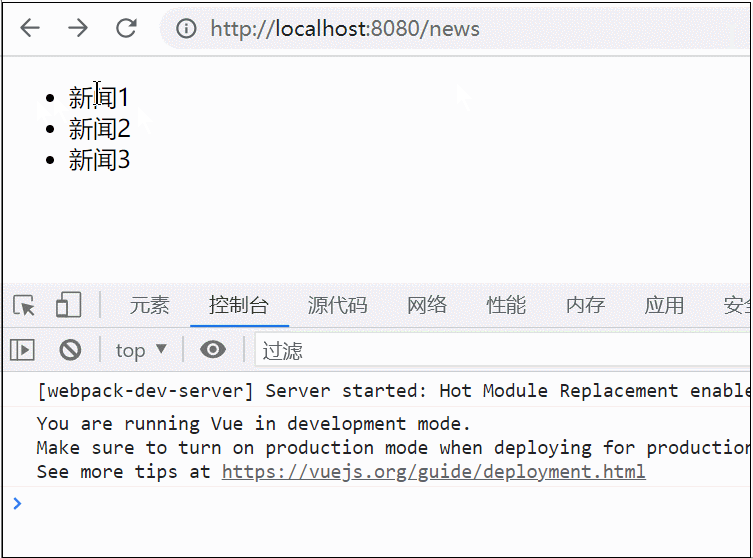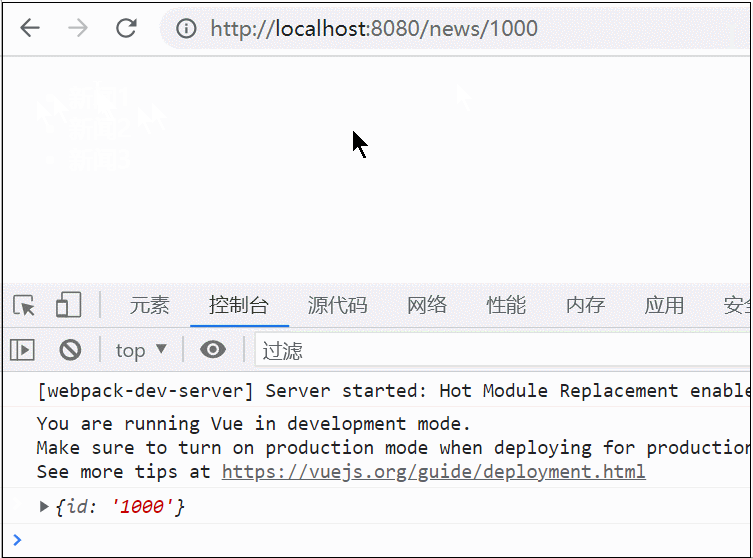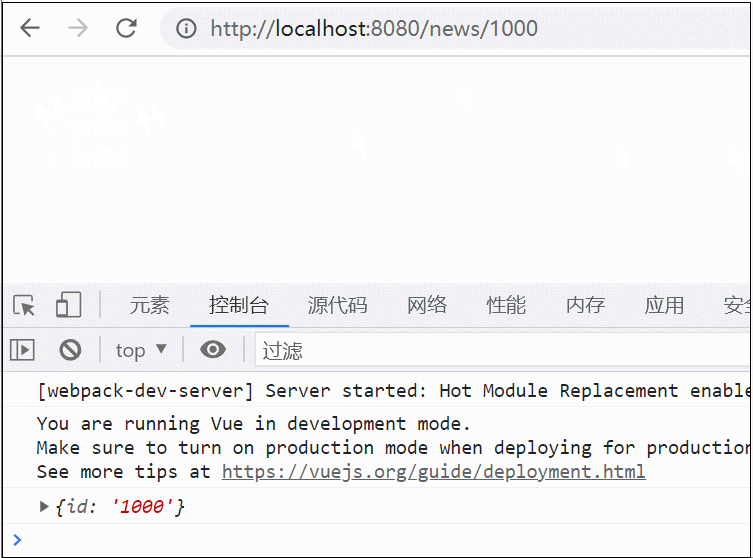
可以看到筛选出来了message中的偶数,现在在控制台打印出message看看
可以看到,message并没有变,还是原来的message,然后在控制台中修改message试试,
修改后我并没有人为的触发任何函数,左边的显示就变成了新的数组的偶数选集
3. 区别
methods是一种交互方法,通常是把用户的交互动作写在methods中;而computed是一种数据变化时mvc中的module 到 view 的数据转化映射。
简单点讲就是methods是需要去人为触发的,而computed是在检测到data数据变化时自动触发的,还有一点就是,性能消耗的区别,这个好解释。
首先,methods是方式,方法计算后垃圾回收机制就把变量回收,所以下次在要求解筛选偶数时它会再次的去求值。而computed会是依赖数据的,就像闭包一样,数据占用内存是不会被垃圾回收掉的,所以再次访问筛选偶数集,不会去再次计算而是返回上次计算的值,当data中的数据改变时才会重新计算。简而言之,methods是一次性计算没有缓存,computed是有缓存的计算。
4. TodoList例子
看了一下Vue官网的todo例子,好像没有筛选功能,所以就写了有个筛选功能的例子,下面代码中,@click的意思是v-on='click'的简写,:class=的意思是v-bind:'class'=的简写
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>todos</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.4.2/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.wrap{
width: 400px;
background-color: #ccc;
margin: 0 auto;
}
i{
color: #f00;
font-size: 12px;
margin-left: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
i:hover{
font-weight: 700;
}
ol{
/*white-space: nowrap;*/
word-wrap:break-word;
}
.done{
text-decoration: line-through;
}
.not{
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrap" id="todos">
<input type="text" v-model='nextItem' @keyup.enter='append'>
<button id="append" @click='append'>添加</button>
<ol>
<li v-for='(item,index) of comp'
:key=item.id
:class='item.state ? "not" : "done"'>
{{item.text}}
<i @click='remove(index)'>完成</i>
</li>
</ol>
<button @click='all'>全部</button>
<button @click='done'>已完成</button>
<button @click='todos'>待完成</button>
</div>
</body>
<script>
var todos = new Vue({
el:'#todos',
data:{
nextItem: '',
nextID: 1,
list: [],
type: null,
},
computed:{
comp:function(){
if( this.type === 0 ){
return this.list;
}
else if(this.type === 1){ //show all
return this.list.filter(function(item){
return true;
})
}
else if(this.type === 2){ //done
return this.list.filter(function(item){
return item.state ? false : true;
})
}
else if(this.type === 3){ //todos
return this.list.filter(function(item){
return item.state ? true : false;
})
}
}
},
methods:{
append:function(){//添加到todo
this.list.push({
id:this.nextID++,
text:this.nextItem,
state: true,
});
this.nextItem = '';
this.type = 0;
},
remove:function(index){ //添加到donelist
this.list[index].state = !this.list[index].state;
},
all:function(){
this.type = 1;
},
done:function(){
this.type = 2;
},
todos:function(){
this.type = 3;
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
到此这篇关于详解Vue的computed(计算属性)如何使用实例之TodoList就介绍到这了。有信念不一定成功,没信念一定会失败。更多相关详解Vue的computed(计算属性)如何使用实例之TodoList内容请查看相关栏目,小编编辑不易,再次感谢大家的支持!