秋天,那永远是蓝湛湛的天空,会突然翻脸而露出险恶的颜色,热带台风夹着密云暴雨,洪水潜流着,复苏的草原又泛起点点苍苍的颜色。然而,台风暴雨一闪而过,强烈的气流依然抖动着耀眼的波光。这时,只有北来的候鸟知道这张温暖的床眠,那飞翔的天鹅、鸿雁和野鸭,就像一片阴深的云朵,使这儿显得更苍郁了。
前言
经常看到讲解Vue2的虚拟Dom diff原理的,但很多都是在原代码的基础上添加些注释等等,这里从0行代码开始实现一个Vue2的虚拟DOM
实现VNode
src/core/vdom/Vnode.js
export class VNode{
constructor (
tag, //标签名
children,//孩子[VNode,VNode],
text, //文本节点
elm //对应的真实dom对象
){
this.tag = tag;
this.children = children
this.text = text;
this.elm = elm;
}
}
export function createTextNode(val){
//为什么这里默认把elm置为undefined,不直接根据tag 用document.createElement(tagName)把elm赋值?而要等后面createElm时候再赋值呢?
return new VNode(undefined,undefined,String(val),undefined)
}
export function createCommentNode(tag,children){
if(children){
for(var i=0;i<children.length;i++){
var child = children[i];
if(typeof child == 'string'){
children[i] = createTextNode(child)
}
}
}
return new VNode(tag,children,undefined,null)
}
定义一个Vnode类, 创建节点分为两类,一类为text节点,一类非text节点
src/main.js
import {VNode,createCommentNode} from './core/vdom/vnode'
var newVonde = createCommentNode('ul',[createCommentNode('li',['item 1']),createCommentNode('li',['item 2']),createCommentNode('li',['item 3'])])
在main.js就可以根据Vnode 生成对应的Vnode对象,上述代码对应的dom表示
<ul> <li>item1</li> <li>item2</li> <li>item3</li> </ul>
先实现不用diff把Vnode渲染到页面中来
为什么先来实现不用diff渲染Vnode的部分,这里也是为了统计渲染的时间,来表明一个道理。并不是diff就比非diff要开,虚拟DOM并不是任何时候性能都比非虚拟DOM 要快
先来实现一个工具函数,不熟悉的人可以手工敲下代码 熟悉下
// 真实的dom操作
// src/core/vdom/node-ops.js
export function createElement (tagName) {
return document.createElement(tagName)
}
export function createTextNode (text) {
return document.createTextNode(text)
}
export function createComment (text) {
return document.createComment(text)
}
export function insertBefore (parentNode, newNode, referenceNode) {
parentNode.insertBefore(newNode, referenceNode)
}
export function removeChild (node, child) {
node.removeChild(child)
}
export function appendChild (node, child) {
node.appendChild(child)
}
export function parentNode (node) {
return node.parentNode
}
export function nextSibling (node) {
return node.nextSibling
}
export function tagName (node) {
return node.tagName
}
export function setTextContent (node, text) {
node.textContent = text
}
export function setAttribute (node, key, val) {
node.setAttribute(key, val)
}
src/main.js
import {VNode,createCommentNode} from './core/vdom/vnode'
import patch from './core/vdom/patch'
var container = document.getElementById("app");
var oldVnode = new VNode(container.tagName,[],undefined,container);
var newVonde = createCommentNode('ul',[createCommentNode('li',['item 1']),createCommentNode('li',['item 2']),createCommentNode('li',['item 3'])])
console.time('start');
patch(oldVnode,newVonde); //渲染页面
console.timeEnd('start');
这里我们要实现一个patch方法,把Vnode渲染到页面中
src/core/vdom/patch.js
import * as nodeOps from './node-ops'
import VNode from './vnode'
export default function patch(oldVnode,vnode){
let isInitialPatch = false;
if(sameVnode(oldVnode,vnode)){
//如果两个Vnode节点的根一致 开始diff
patchVnode(oldVnode,vnode)
}else{
//这里就是不借助diff的实现
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm;
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm);
createElm(
vnode,
parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
if(parentElm != null){
removeVnodes(parentElm,[oldVnode],0,0)
}
}
return vnode.elm;
}
function patchVnode(oldVnode,vnode,removeOnly){
if(oldVnode === vnode){
return
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
const oldCh = oldVnode.children;
const ch = vnode.children
if(isUndef(vnode.text)){
//非文本节点
if(isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)){
//都有字节点
if(oldCh !== ch){
//更新children
updateChildren(elm,oldCh,ch,removeOnly);
}
}else if(isDef(ch)){
//新的有子节点,老的没有
if(isDef(oldVnode.text)){
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm,'');
}
//添加子节点
addVnodes(elm,null,ch,0,ch.length-1)
}else if(isDef(oldCh)){
//老的有子节点,新的没有
removeVnodes(elm,oldCh,0,oldCh.length-1)
}else if(isDef(oldVnode.text)){
//否则老的有文本内容 直接置空就行
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm,'');
}
}else if(oldVnode.text !== vnode.text){
//直接修改文本
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm,vnode.text);
}
}
function updateChildren(parentElm,oldCh,newCh,removeOnly){
//这里认真读下,没什么难度的,不行的话 也可以搜索下图文描述这段过程的
let oldStartIdx = 0;
let newStartIdx =0;
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length -1;
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0];
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx];
let newEndIdx = newCh.length-1;
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let refElm;
const canMove = !removeOnly
while(oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx){
if(isUndef(oldStartVnode)){
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
}else if(isUndef(oldEndVnode)){
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
}else if(sameVnode(oldStartVnode,newStartVnode)){
patchVnode(oldStartVnode,newStartVnode)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}else if(sameVnode(oldEndVnode,newEndVnode)){
patchVnode(oldEndVnode,newEndVnode)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx];
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx];
}else if(sameVnode(oldStartVnode,newEndVnode)){
patchVnode(oldStartVnode,newEndVnode);
//更换顺序
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm,oldStartVnode.elm,nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
}else if(sameVnode(oldEndVnode,newStartVnode)){
patchVnode(oldEndVnode,newStartVnode)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm,oldEndVnode.elm,oldStartVnode.elm)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}else{
createElm(newStartVnode,parentElm,oldStartVnode.elm)
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx];
}
}
if(oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx){
//老的提前相遇,添加新节点中没有比较的节点
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx+1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm,refElm,newCh,newStartIdx,newEndIdx)
}else{
//新的提前相遇 删除多余的节点
removeVnodes(parentElm,oldCh,oldStartIdx,oldEndIdx)
}
}
function removeVnodes(parentElm,vnodes,startIdx,endIdx){
for(;startIdx<=endIdx;++startIdx){
const ch = vnodes[startIdx];
if(isDef(ch)){
removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
}
function addVnodes(parentElm,refElm,vnodes,startIdx,endIdx){
for(;startIdx <=endIdx;++startIdx ){
createElm(vnodes[startIdx],parentElm,refElm)
}
}
function sameVnode(vnode1,vnode2){
return vnode1.tag === vnode2.tag
}
function removeNode(el){
const parent = nodeOps.parentNode(el)
if(parent){
nodeOps.removeChild(parent,el)
}
}
function removeVnodes(parentElm,vnodes,startIdx,endIdx){
for(;startIdx<=endIdx;++startIdx){
const ch = vnodes[startIdx]
if(isDef(ch)){
removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
}
function isDef (s){
return s != null
}
function isUndef(s){
return s == null
}
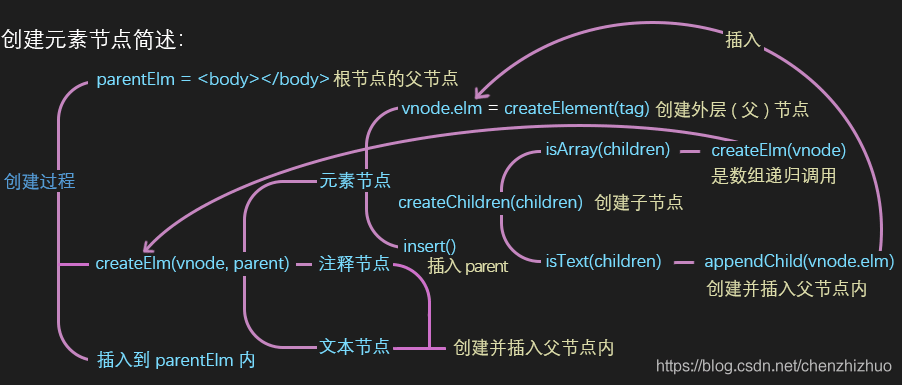
function createChildren(vnode,children){
if(Array.isArray(children)){
for(let i=0;i<children.length;i++){
createElm(children[i],vnode.elm,null)
}
}
}
function createElm(vnode,parentElm,refElm){
const children = vnode.children
const tag = vnode.tag
if(isDef(tag)){
// 非文本节点
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createElement(tag); // 其实可以初始化的时候就赋予
createChildren(vnode,children);
insert(parentElm,vnode.elm,refElm)
}else{
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createTextNode(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm,vnode.elm,refElm)
}
}
function insert(parent,elm,ref){
if(parent){
if(ref){
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent,elm,ref)
}else{
nodeOps.appendChild(parent,elm)
}
}
}
这就是完整实现了
到此这篇关于深入理解Vue2.x的虚拟DOM diff原理就介绍到这了。世间的捷径只有一条——正道!更多相关深入理解Vue2.x的虚拟DOM diff原理内容请查看相关栏目,小编编辑不易,再次感谢大家的支持!