不管怎样,生活还是要继续向前走去。有的时候伤害和失败不见得是一件坏事,它会让你变得更好,孤单和失落亦是如此。每件事到最后一定会变成一件好事,只要你能够走到最后。纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。
本文实例为大家分享了Vue实现简易购物车的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
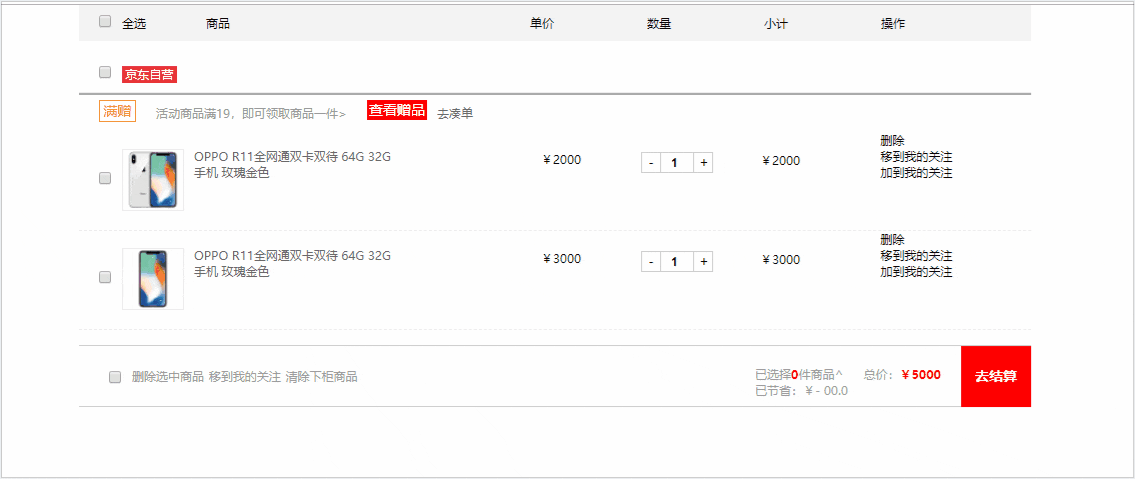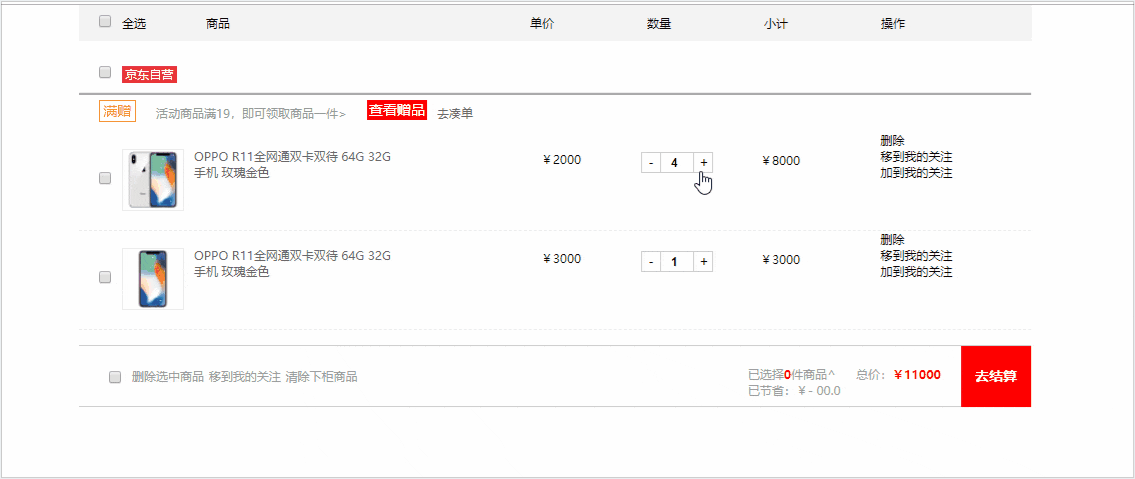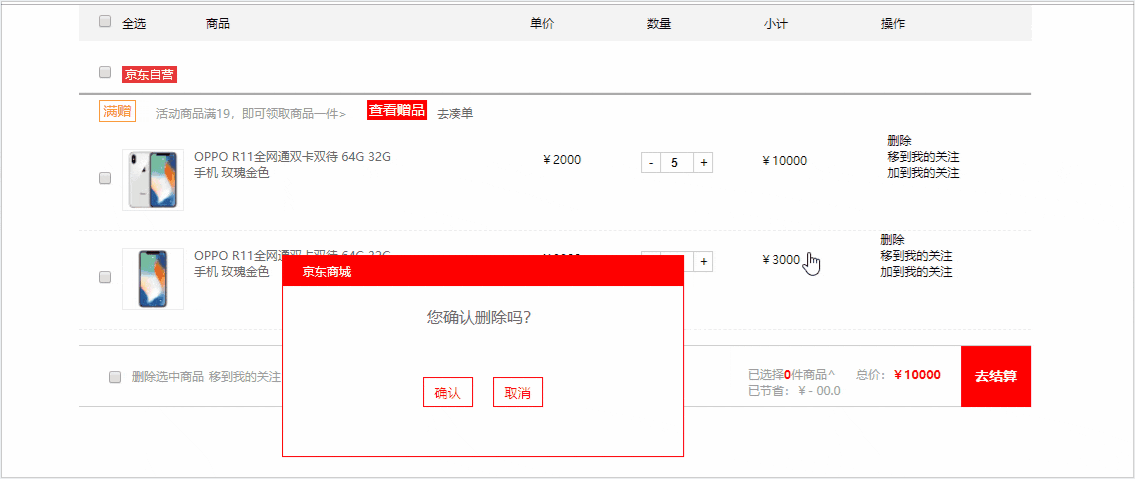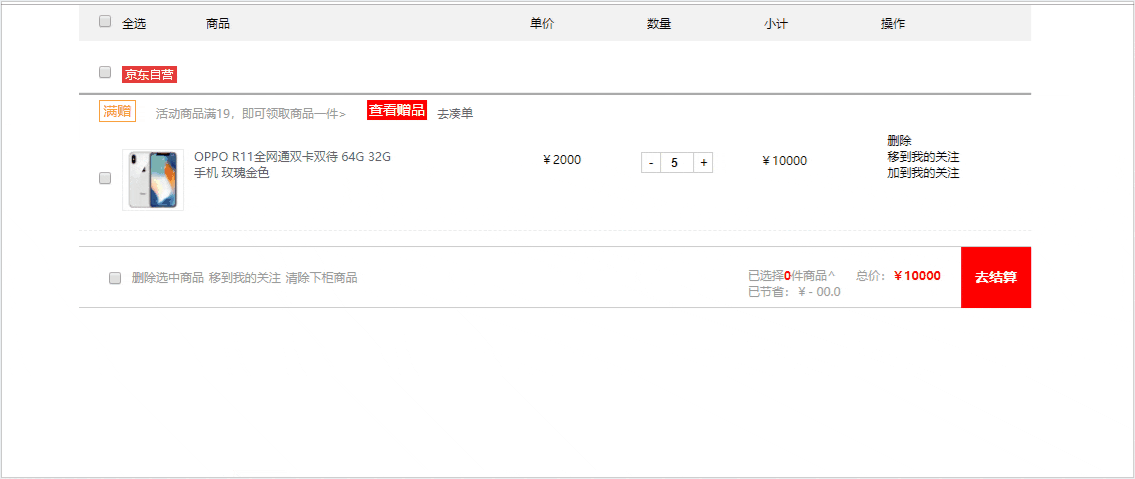
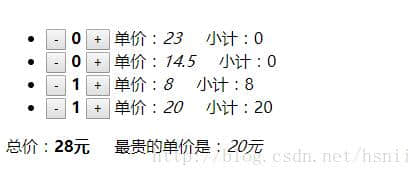
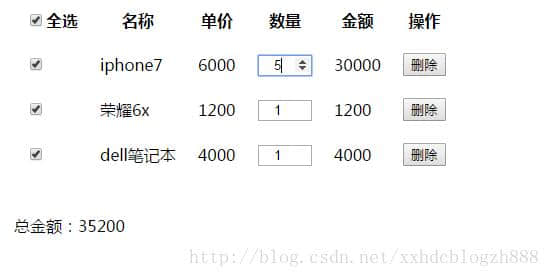
先来看一下完成后的效果吧。
CSS 部分
这里没什么好说的,就是v-cloak 这一个知识点
table{
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
th,td{
padding: 8px 16px;
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
text-align: center;
}
th{
background-color: #f7f7f7;
color: #5c6b77;
font-weight: 600;
}
[v-cloak]{
display: none;
}
HTML部分
这里说明一些用到的一些Vue的知识点:
- v-if
- v-for
- v-cloak
- v-on > @
- v-bind > :
- 方法 methods
- 计算属性 computed
- 过滤器 filters
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>购物车</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" rel="nofollow noopener noreferrer" href="style.css" >
</head>
<body>
<div id="app" v-cloak>
<div v-if="books.length">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>书籍名称</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>删除</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in books">
<th>{{item.id}}</th>
<th>{{item.name}}</th>
<th>{{item.date}}</th>
<!--方案一 保留小数点和货币符号-->
<!-- <th>{{"¥"+item.price.toFixed(2)}}</th> -->
<!--方案二-->
<!-- <th>{{getFinalPrice(item.price)}}</th> -->
<!--方案三-->
<th>{{item.price | showPrice}}</th>
<th>
<button @click="decrement(index)" :disabled="item.count<=0">-</button>
{{item.count}}
<button @click="increment(index)">+</button>
</th>
<th><button @click="removeHandle(index)">移除</button></th>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h2>总价格:{{totalPrice | showPrice}}</h2>
</div>
<h2 v-else>
购物车为空
</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="main.js"></script>
</html>
JS部分
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
books:[
{
id:1,
name:"《算法导论》",
date:'2006-9',
price:85.00,
count:1
},
{
id:2,
name:"《UNIX编程艺术》",
date:'2006-2',
price:50.00,
count:1
},
{
id:3,
name:"《编程艺术》",
date:'2008-10',
price:39.00,
count:1
},
{
id:4,
name:"《代码大全》",
date:'2006-3',
price:128.00,
count:1
},
]
},
methods: {
//这里我们放弃使用方法的形式来求总价格,转而使用计算属性,因为它的效率更高。
// getFinalPrice(price){
// return "¥"+price.toFixed(2)
// },
increment(index){
this.books[index].count++
},
decrement(index){
this.books[index].count--
},
removeHandle(index){
this.books.splice(index,1);
}
},
computed: {
totalPrice(){
// 方案一:普通的for循环
// let totalPrice = 0;
// for(let i=0;i<this.books.length;i++){
// totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count
// }
// return totalPrice
// 方案二:for in
// let totalPrice = 0;
// for(let i in this.books){
// // console.log(i);//1 2 3 4
// totalPrice += this.books[i].price * this.books[i].count
// }
// return totalPrice
// 方案三:for of
// let totalPrice = 0;
// for(let item of this.books){
// // console.log(item);//这里拿到的就是数组里的每个对象
// totalPrice += item.price * item.count
// }
// return totalPrice
// 方案四:reduce
return this.books.reduce(function (preValue, book) {
// console.log(book);//分别输出四个对象
return preValue + book.price * book.count
}, 0)
}
},
// 过滤器
filters:{
showPrice(price){
return "¥"+price.toFixed(2)
}
}
})
到此这篇关于Vue如何实现简易购物车案例就介绍到这了。人生大投资绝不要犹豫:健康和教育!更多相关Vue如何实现简易购物车案例内容请查看相关栏目,小编编辑不易,再次感谢大家的支持!