Unirest
Unirest是一个轻量级的 HTTP 请求库,可发起 GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS 请求。
支持 Node、Ruby、Java、PHP、Python、Objective-C、.NET 等多种语言。
底层是基于httpclient,所以使用Unirest之前先要引入httpclient相关的依赖。
Maven项目可以直接在pom.xml文件中引入Unirest 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mashape.unirest</groupId>
<artifactId>unirest-java</artifactId>
<version>1.4.9</version>
</dependency>底层是基于httpclient的,所以需要引入httpclient相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpasyncclient</artifactId>
<version>4.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpmime</artifactId>
<version>4.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.json</groupId>
<artifactId>json</artifactId>
<version>20140107</version>
</dependency>测试相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>6.13.1</version>
</dependency>创建Post连接格式:
HttpResponse<JsonNode> jsonResponse = [Unirest.post(](https://link.jianshu.com?t=http://Unirest.post()"[http://httpbin.org/post](https://link.jianshu.com?t=http://httpbin.org/post)")
.header("accept", "application/json")
.queryString("apiKey", "123")
.field("parameter", "value")
.field("foo", "bar")
.asJson();请求
- .header 请求头;
- .field 添加的参数;
- .queryString设置的键值对;
如果参数进行了包装,可以直接传.body();或者利用键值对的形式.field(),利用map的格式来传送参数。多个header,可以同样如此。
响应
在接收到响应Unirest以对象的形式返回结果时,对于响应细节,该对象应该始终具有与每种语言相同的键。
- .getStatus() - HTTP响应状态代码(示例:200)
- .getStatusText() - HTTP响应状态文本(示例:“OK”)
- .getHeaders() - HTTP响应标头
- .getBody() - 解析响应正文(如适用),例如JSON响应将解析为对象/关联数组。
- .getRawBody() - 未解析的响应正文
注意:
- 使用Unirest请求的数据一般是 JsonNode,若返回类型报错,一般为String,最后得到的为.asString();
- .header用了设置header的各种参数,包括token
- .routeParam用于设置路径中带有参数的如{cid}之类的
- .paramString用于设置get命令中 &的键值对
- .field用于设置post的参数,也可以直接用一个map,.fields(prams) //prams是一个map,put了很多参数进去,和直接多个fields一样的效果
- 返回的结果打印一般用,response.getBody( ).getObject( ) 得到的JSON对象,之后的JSON解析出需要的内容都是以此为基础分层剥离。
- 返回的状态用response.getStatus(),即返回的状态码,注意有个别成功码并不一样,如前台是200,后台是302
以下用一个简单的例子介绍Unirest的使用
场景:
从文件中读取json报文,并将报文中的部分字段进行随机参数化。
使用unirest发送post请求并将json字符串作为参数传入。最后将响应报文中的部分字段提取并输出。
这里提供testng的两种方式发送多次post请求,并保证每次请求都是一个新的实例。
上代码
1、在maven工程的src/main/resources下新增文件 pushClaim.txt,存放post请求内容
2、在maven工程的src/main/resources下新增prop.properties文件,用于维护请求路径,方便后期修改
claimPushFilePath = ./src/main/resources/pushClaim.txt pushClaimUrl = //…:8080//services/restful/claim/*
3、引入unirest相关依赖,上面有介绍,这里不再复述。
4、在maven工程的src/main/java下新增目录 com/unirest用于存放相关java类
1)新增ClaimTemp类,主要是读取prop.properties文件,并替换pushClaim.txt中json字符串中部分需要参数化的字段为指定格式
package com.unirest;
import com.sc.util.ConfigurationUtil;
import org.apache.commons.configuration.Configuration;
import java.io.*;
public class ClaimTemp {
public static final Configuration file = ConfigurationUtil.getCommonsPropertis("prop.properties");
public static final String filePath = file.getString("claimPushFilePath");
public static final String pushClaimUrl = file.getString("pushClaimUrl");
public static final String loginUrl = file.getString("loginUrl");
public static final String openClaimTaskUrl = file.getString("openClaimTaskUrl");
public String readFile() throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "UTF-8"));
String aline = null;
while((aline = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null ){
sb.append(aline).append( "\n");
}
} finally {
if(inputStream!= null){
inputStream.close();
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString()) ;
return sb.toString();
}
public String getClaimJsonStr(String userAccount,String accidentNo, String claimNo,String claimCompanyId, String lossVehicleType ,String vin)throws IOException{
String strJson = readFile();
String claimTemplate = strJson.replace("=claimCompanyId=",claimCompanyId)
.replace("=accidentNo=",accidentNo)
.replace("=estimator=",userAccount)
.replace("=claimNo=",claimNo)
.replace("=lossVehicleType=",lossVehicleType)
.replace("=vin=",vin);
return claimTemplate;
}
}2)新增ClaimJSONGenerator类,用于替代json字符串中需要参数化的字段,这里使用随机数
package com.unirest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class ClaimJSONGenerator {
private String accidentNo;
private String claimNo;
String strDate;
String newClaimJson;
int random;
Date date;
SimpleDateFormat sdf;
public ClaimJSONGenerator() {
date = new Date();
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("MMddhhmmssSSS");
strDate = sdf.format(date);
random = (int) Math.random() * 1000 + 1;
accidentNo = "APD83_acc_" + strDate + random;
claimNo = "APD83_claim_" + strDate + random;
}
public String getNewClaimJSON(String userAccount, String lossVehicleType, String vin,String claimCompanyId) throws IOException {
ClaimTemp ct = new ClaimTemp();
newClaimJson = ct.getClaimJsonStr(userAccount,accidentNo,claimNo,claimCompanyId,lossVehicleType,vin);
return newClaimJson;
}
}3)上述提到使用testng的两种方式发送多次post请求,这里一一介绍 方法一:使用DataProvider注释
@DataProvider(name ="pushParam")
public Object[][] pushClaim(){
int claimCount = 1 ;
Object[][] objects = new Object[claimCount][];
Random random = new Random();
for(int i =0 ;i<claimCount;i++){
int num = random.nextInt(999999);
objects[i] = new Object[]{"vip","01","LSVDM49F2"+num,"2345"};
}
return objects;
}测试类
@Test(dataProvider = "pushParam",dataProviderClass = ClaimFactory.class)
public void testDataProvider(String account,String lossVehicleType,String vin,String claimCompanyId) throws IOException, UnirestException {
System.out.println(account+"--------------"+lossVehicleType+"--------------"+vin+"--------------"+claimCompanyId);
HttpResponse<JsonNode> jsonResponse = Unirest.post(ClaimTemp.pushClaimUrl)
.header("Content-Type","application/json")
.body(new ClaimJSONGenerator().getNewClaimJSON(account,lossVehicleType,vin,claimCompanyId))
.asJson();
//输出响应正文
String s =jsonResponse.getBody().toString();
String accidentNo = jsonResponse.getBody().getObject().get("accidentNo").toString();
String resultCode = jsonResponse.getBody().getObject().get("resultCode").toString();
System.out.println(s+"-----------");
System.out.println(accidentNo+"-----------"+resultCode);
}使用Factory注释
import org.testng.annotations.Factory;
import java.util.Random;
public class ClaimFactory {
@Factory
public Object[] createInstances(){
int claimCount = 1 ;
Object[]objects = new Object[claimCount];
Random random = new Random();
for(int i =0 ;i<claimCount;i++){
int num = random.nextInt(999999);
String account = "vip";
String lossVehicleType = "01";
String vin = "LSVDM49F2"+num;
String claimCompanyId = "2345";
objects[i] = new UnirestApiTest(account,lossVehicleType,vin,claimCompanyId);
}
return objects;
}
}package com.unirest;
import com.mashape.unirest.http.HttpResponse;
import com.mashape.unirest.http.JsonNode;
import com.mashape.unirest.http.Unirest;
import com.mashape.unirest.http.exceptions.UnirestException;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class UnirestApiTest {
private String account;
private String lossVehicleType;
private String vin;
private String claimCompanyId;
public UnirestApiTest(String account,String lossVehicleType,String vin,String claimCompanyId ){
this.account = account;
this.lossVehicleType = lossVehicleType;
this.vin = vin;
this.claimCompanyId = claimCompanyId;
}
@Test
public void testFactory() throws IOException, UnirestException {
System.out.println(account+"--------------"+lossVehicleType+"--------------"+vin+"--------------"+claimCompanyId);
HttpResponse<JsonNode> jsonResponse = Unirest.post(ClaimTemp.pushClaimUrl)
.header("Content-Type","application/json")
.body(new ClaimJSONGenerator().getNewClaimJSON(account,lossVehicleType,vin,claimCompanyId))
.asJson();
//输出响应正文
String s =jsonResponse.getBody().toString();
String accidentNo = jsonResponse.getBody().getObject().get("accidentNo").toString();
String resultCode = jsonResponse.getBody().getObject().get("resultCode").toString();
System.out.println(s+"-----------");
System.out.println(accidentNo+"-----------"+resultCode);
}
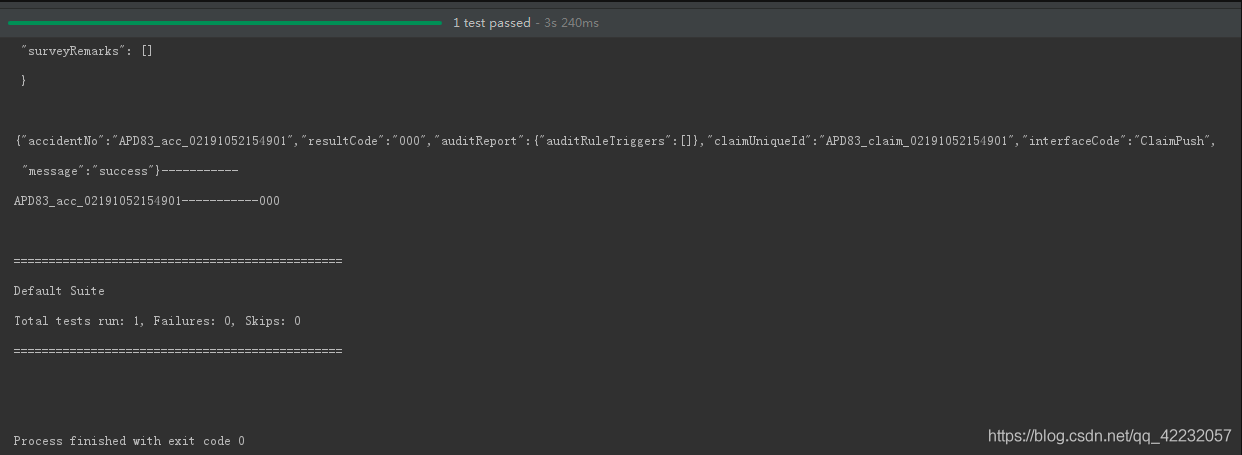
}这种方式运行直接运行ClaimFactory 类,输出结果:
到此这篇关于关于Java使用Http轻量级请求库Unirest的方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Http轻量级请求库Unirest内容请搜索好代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好代码网!


