概述
多态性 (polymorphism) 是面向对象程序设计的一个重要特征 利用多态性扩展设计和实现一个易于扩展的系统 C++ 中多态性:同一函数名可以实现
概述
多态性 (polymorphism) 是面向对象程序设计的一个重要特征. 利用多态性扩展设计和实现一个易于扩展的系统.

C++ 中多态性:
- 同一函数名可以实现不同的功能
- 用一个函数名调用不同内容的函数完成不同的工作
静态多态
静态多态 (static polymorphism) 是通过函数的重载实现的, 包括函数的重载和运算符重载. 在程序编译时系统就能觉得调用哪个函数.
函数重载
int main() {
cout << max(1,2) << endl;
cout << max(1.2, 2.3) << endl;
return 0;
}
int max(int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a:b;
}
double max(double a, double b){
return (a > b) ? a:b;
}
输出结果:
2
2.3
运算符重载
int main() {
Complex c1(2, 4), c2(6, 10);
c1 = c1 + c2;
c1.display();
return 0;
}
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c) {
return Complex(real + c.real, imag + c.imag);
}
输出结果:
(8, 14i)
动态多态
动态多态 (dynamic polymorphism) 是在程序运行中才动态地确定操作所针对的对象.
非动态
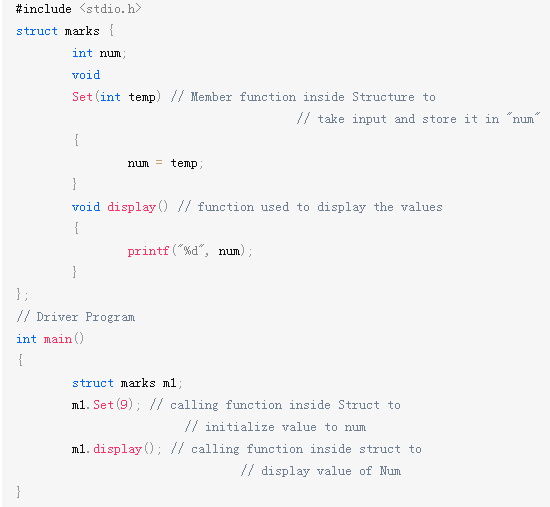
Person 类:
#ifndef PROJECT6_PERSON_H
#define PROJECT6_PERSON_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name; // 姓名
char gender; // 性别
public:
Person(string n, char g) : name(n), gender(g) {}
void display() {
cout << "name: " << name << endl;
cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;
}
};
#endif //PROJECT6_PERSON_H
Teacher 类:
#ifndef PROJECT6_TEACHER_H
#define PROJECT6_TEACHER_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Person.h"
using namespace std;
class Teacher : public Person {
private:
string title; // 头衔
public:
Teacher(string n, char g, string t) : Person(n, g), title(t) {}
void display() {
Person::display();
cout << "title: " << title << endl;
}
};
#endif //PROJECT6_TEACHER_H
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Person.h"
#include "Teacher.h"
int main() {
// 创建对象
Person p1("王叔叔", 'm'), *pt; // 指针类型为
Teacher t1("王老师", 'f', "教导主任");
pt = &p1;
pt->display();
pt = &t1;
pt->display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
name: 王叔叔
gender: m
name: 王老师
gender: f
我们可以发现 Teacher 对象的头衔并没有输出, 因为 pt 指针的类型是 Person, 调用的是 Person 的display()函数.
动态
我们把show()函数声明为虚函数.
Person 类:
#ifndef PROJECT6_PERSON_H
#define PROJECT6_PERSON_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name; // 姓名
char gender; // 性别
public:
Person(string n, char g) : name(n), gender(g) {}
virtual void display() {
cout << "name: " << name << endl;
cout << "gender: " << gender << endl;
}
};
#endif //PROJECT6_PERSON_H
main:
#include <iostream>
#include "Person.h"
#include "Teacher.h"
int main() {
// 创建对象
Person p1("王叔叔", 'm'), *pt; // 指针类型为
Teacher t1("王老师", 'f', "教导主任");
pt = &p1;
pt->display();
pt = &t1;
pt->display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
name: 王叔叔
gender: m
name: 王老师
gender: f
title: 教导主任
到此这篇关于C/C++中多态性详解及其作用介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++多态性内容请搜索好代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好代码网!